
CONCLUSION

The importance of fuzzy logic in the design of intelligent
GIS is illustrated in this approach. At the opposite of map
algebra systems based on boolean logic, this system manages imprecise and
uncertain information in an efficient manner:
- the fuzzy reasoning allows some
problems to be solved without critical choice and provides more information
about a particular fact because fuzzy sets characterize it precisely,
- rapid fuzzy inferences transform
the system in a real time system. The simple generalized modus ponens fast
algorithm allows a gain of chip operations from
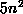 (n is the number of elements of universes) to about ten operations.
Equally the parallel generalized modus ponens
fast algorithm allows a gain of chip operations from
(n is the number of elements of universes) to about ten operations.
Equally the parallel generalized modus ponens
fast algorithm allows a gain of chip operations from 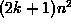 (k is the number of parallel rules) to about k ten operations,
(k is the number of parallel rules) to about k ten operations,
- the easy specification (with several kinds of rules) or modification
of a problem allows an expert or a user to specify and solve his problem
by using a formal language and approach
the best solution step by step.
We are now looking for :
- the integration of spatial rules using spatial relations which are
fuzzy relations between two or more geographical objects such as "north
of", "inside", "near to", "along", ....
- managing consistency and redundancy of rules in the parametric computation
for parallel rules.
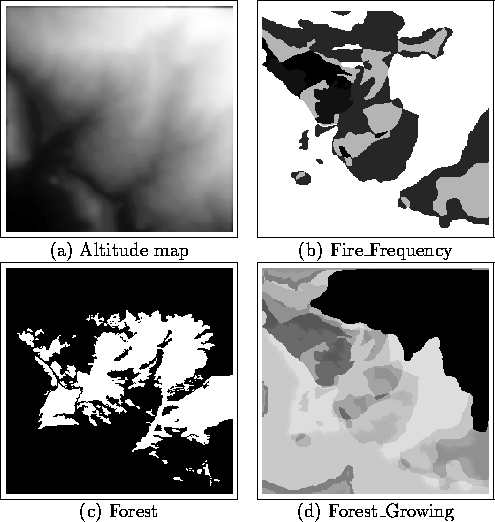
Figure 10: Data maps and result map.



IRIT-UPS


![]()
![]()