 |
 |
![]()
Contrast between two pixels is given by the amplitude of the difference
between two color vectors v and w:
Fuzzy concept is expressed by means of a ``membership of a fuzzy subset''
function, expressed by:
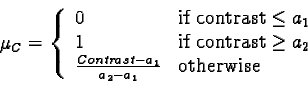 |
This function is applied to two values of contrasts:
The values of thresholds a1 and a2, differ for each type of contrast. To avoid favouring a contrast in particular, the two values are amalgamated by an average operator which gives a criterion of homogeneity: if it is lower than a given threshold, the pixel considered is amalgamated in the area.
The approaches presented above are particularly adapted to a local processing starting from a ``seed'' point. For a more global processing, ``Split and merge'' technique is used:
This processing has certain similarities to a process of classification.
The preliminary phase of ``splitting'' makes it possible to limit the number
of aggregations and also to better tolerate small disparities, because
the aggregation is done starting from average values. The order in which
are considered the areas for the aggregation influences the final result.