
In
Summary

Quantified adaptive fusion has the advantage:
- of using conjunctive fusion as often as possible (the most adapted
to our problem) (as long as a consensus among at least part of the sources
can be found). When a total conflict occurs between all the sources, disjunctive
fusion, the only applicable method, is used. However, with a great number
of sources, it becomes difficult to have all the sources, in conflict,
at the same time.
- of managing properly the conflict, avoiding to use often disjunctive
fusion;
- of having a rather reasonable execution time (the operators
used (min and max) are inexpensive)
On the other hand, this operator has the following defaults:
- its complexity in
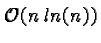 because of the calculation of the degree of consensus h between
sources;
because of the calculation of the degree of consensus h between
sources;
- its instability when the possibility distributions have a very
weak intersection or are very close without having intersection;
- it is not associative: the order of fusion of sources is significant
if fusion is performed by group of two sources at the same time, and this
can be avoided by performing the fusion of all the sources as a whole.



IRIT-UPS


![]()
![]()