
How can we conceive an aerial photograph and/or a remote sensing image?
|
| A. As a set of fundamental photorecognition elements |
|
| B. As a registration of sets of : | |
| defined in terms of the way they reflect or emit radiation in different time (years, seasons, hours) and different wavelengths. | |
| By combining the photorecognition elements with the recognition of specific point, line, polygon and spatial features –as shown in the following table- we can facilitate interpretation and information extraction. | |
|
| The photointerpreter’s “function” in applying remote sensing/photointerpretation methodologies generally follows the procedure below: |
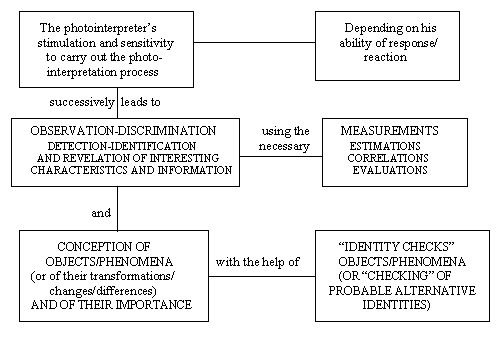 |
The photointerpreter’s mental stimulation, enabling him/her to carry out the photointerpretation process, results from: |
a. his reaction/response to the image/a pair of remotely sensed images basic data: |
|
It is obvious that the remotely sensed images of an area/region could be: |
The analysis of these remotely sensed images can be carried out either using analogue photointerpretation, or digital methods and techniques, or by a combination of the methods mentioned above. Although the basic image data are a point of reference during the analogue/digital process of the revelation/“identity check” of objects/phenomena and in working out of the relevant problems, it is obvious that the exploitation of these data depends on the possibilities and the restrictions of the methods and practices selected and on the information/infrastructure available. |
|
National Technical University of Athens |