
Principle

The criterion allowing to determine
which fusion to use is the height of the intersection
of the various opinions expressed by each source. This height, which corresponds
to a degree of consensus between the sources, is measured by the height
of the intersection between the possibility distributions provided by each
source.
Let us then note that the height h of the intersection of two
possibility distributions 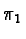 and
and 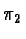 ,
defined onto the referential set
,
defined onto the referential set 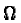 ,
is calculated as follows:
,
is calculated as follows:
- A height of 1 means that the consensus is
total between the sources; fusion will be then conjunctive.
- A height of 0 states there is no agreement
between the sources. Disjunctive fusion is used in this situation
of total conflict.
- A height between 0 and 1 means that there is a partial
agreement, or a partial conflict,
between the sources. In this case, the two kinds of fusion, conjunctive
and disjunctive, are used, but disjunctive fusion is more or less limited
according to the degree of consensus between the sources.
The rule of adaptive fusion is presented in paragraph ``Adaptive
fusion''. Let us then briefly represent its behaviour.
The adaptive fusion of two sources S1 and S2
is defined as follows (figure 31):
Figure 31: Adaptive fusion of two sources in low conflict.
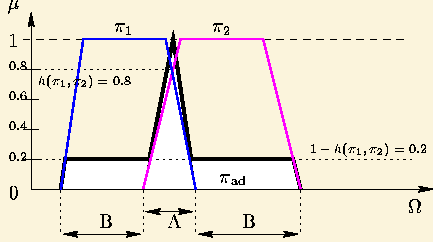 |
- Part A of the rule corresponds
to renormalized conjunctive fusion. It is used when the sources
are in agreement (areas where the distributions
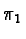 and
and 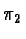 have an intersection).
have an intersection).
- Part B corresponds to the disjunctive
fusion used in the case of conflict between the sources. The importance
attached to this disjunctive fusion varies from 1 (when the conflict is
total) to 0 (when the agreement is total).
This rule was defined to perform the fusion of only two sources.



IRIT-UPS


![]()
![]()
![]() and
and ![]() ,
defined onto the referential set
,
defined onto the referential set ![]() ,
is calculated as follows:
,
is calculated as follows: 