 |
 |
![]()
![]()
It is possible that, among the sources to be fused, some are considered more reliable than others.
For example, the size of an individual can be evaluated either
It is obvious that direct information is more precise than indirect information. In the presence of conflict between direct and indirect sources, confidence will be given rather to the direct sources and information provided by the indirect sources will be discarded.
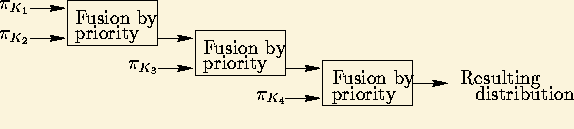
A set of information sources K can be classified according to their reliability.
Let ![]() be a K-partition such that the sources brought together in Ki
are considered to have the same reliability, and to be more reliable than
those of sets Kj with j > i. Information
fusion provided by sets
be a K-partition such that the sources brought together in Ki
are considered to have the same reliability, and to be more reliable than
those of sets Kj with j > i. Information
fusion provided by sets ![]() will be performed as follows (figure 37):
will be performed as follows (figure 37):
 |
Let
We can define a rule for fusion by priority with a conjunctive behaviour
or a disjunctive behaviour.
|
(73) |
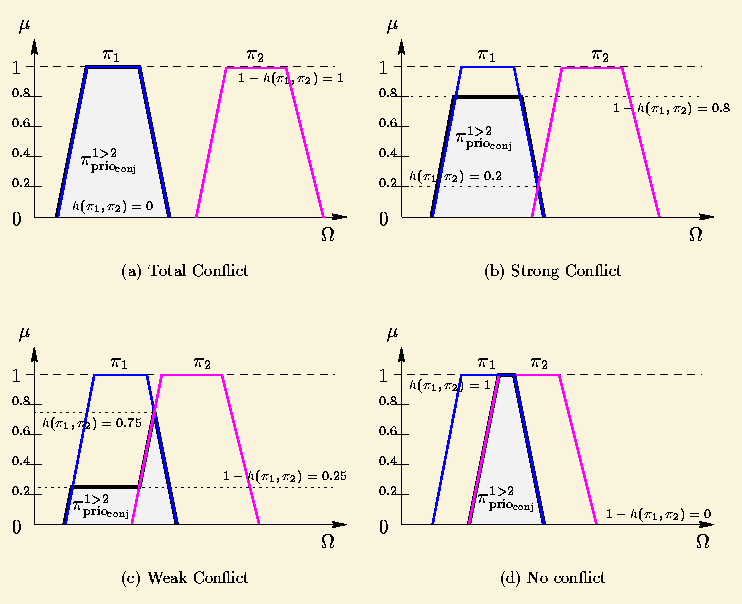
This rule expresses that the sources of set K1 provide reliable information, whereas information resulting from the set K2 is regarded as reliable only with a degree of certainty equal to the degree of consensus h between sets K1 and K2.
This rule corresponds to an operation of weighted conjunction whose weighting
Let us notice that the result of this fusion by priority is under-normalized
as soon as ![]() .
.
|
|
(74) |
This rule expresses that if one of the two sets is supposed mistaken, it is surely the least reliable group K2. So, information brought by K2 is stored only if they are in agreement with K1. The more the conflict between K1 and K2 increases, and the more is truncated the information of K2 to which one makes less confidence. When the conflict is total, only information of K1 will be stored.
Let us notice that the result of this fusion by priority is under-normalized
as soon as ![]() .
.
 |
![]()